Managing Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome
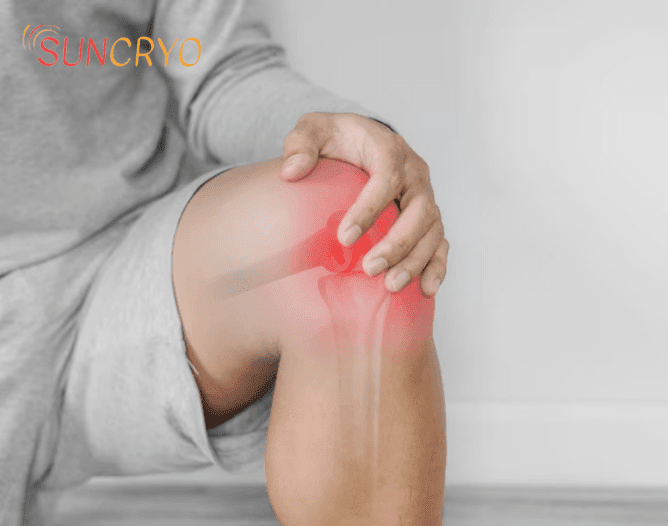
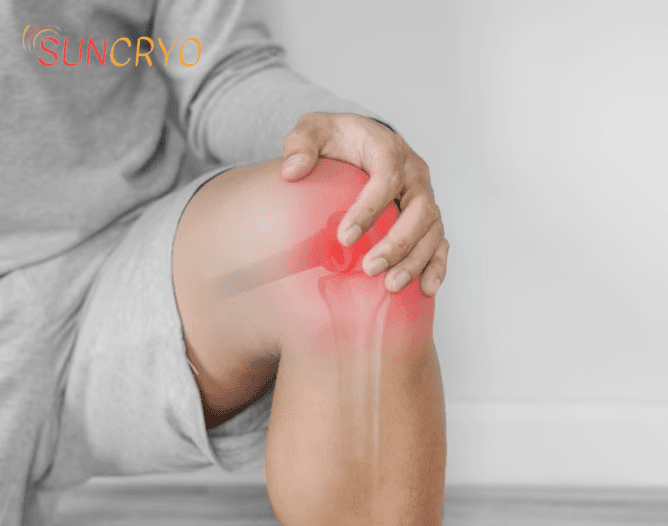
Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome (PFPS) is a common condition characterized by pain around or behind the kneecap (patella) that often arises during activities that involve bending of the knee. At [georgetownsuncryo], we aim to provide comprehensive insights into PFPS, from its causes and risk factors to effective management strategies. Our goal is to empower individuals with knowledge to not only understand this condition but also to take proactive steps towards relief and recovery.
Unveiling the Causes of Patellofemoral Pain
PFPS can be attributed to various factors that contribute to the improper alignment and tracking of the patella within the femoral groove. Some of the key causes include:
1. Muscle Imbalances and Weakness
Muscular imbalances between the quadriceps, hamstrings, and hip muscles can lead to altered patellar movement. Weak quadriceps, in particular, can disrupt the dynamic stability of the knee joint, resulting in increased pressure on the patellofemoral joint during movement.
2. Overuse and High-Impact Activities
Engaging in repetitive high-impact activities such as running, jumping, or squatting can strain the patellofemoral joint, leading to irritation and inflammation. This is especially prevalent in athletes and individuals with physically demanding lifestyles.
3. Malalignment of the Patella
Structural anomalies or abnormal alignment of the patella can contribute to improper tracking and increased friction between the patella and the femoral groove. This friction is a major source of pain in PFPS.
Identifying Risk Factors for PFPS
Several risk factors can increase an individual’s susceptibility to developing PFPS. These include:
1. Biomechanical Factors
Individuals with flat feet, high arches, or abnormal lower limb alignment are more prone to altered patellar tracking, putting them at a higher risk for PFPS.
2. Muscle Tightness
Tightness in the muscles surrounding the knee and hip can disrupt the natural movement of the patella, leading to increased pressure on the patellofemoral joint.
3. Previous Injuries
A history of knee injuries, such as ligament sprains or meniscus tears, can weaken the joint and contribute to the onset of PFPS.
Effectively Managing PFPS
Managing PFPS involves a multi-faceted approach that addresses both symptom relief and underlying causes. Here are some strategies that can help:
1. Strengthening Exercises
Targeted exercises to strengthen the quadriceps, hamstrings, and hip muscles can restore muscular balance and improve knee joint stability. Exercises like leg lifts, squats, and lunges can be highly effective.
2. Flexibility and Mobility Work
Regular stretching of the quadriceps, hamstrings, and iliotibial band can enhance flexibility and alleviate tension around the knee joint.
3. Patellar Taping
Applying adhesive tape to the patella can provide external support, help correct patellar alignment, and reduce pain during physical activities.
4. Orthotic Support
Custom orthotic inserts can correct biomechanical issues and provide proper arch support, helping to align the lower limbs and prevent patellar misalignment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome is a condition that can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. Understanding its causes, risk factors, and effective management strategies is crucial for those seeking relief. At [https://georgetownsuncryo.com/], we are committed to providing valuable insights and actionable information to help individuals overcome PFPS and regain their mobility and comfort. Remember, consult with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance tailored to your specific condition.