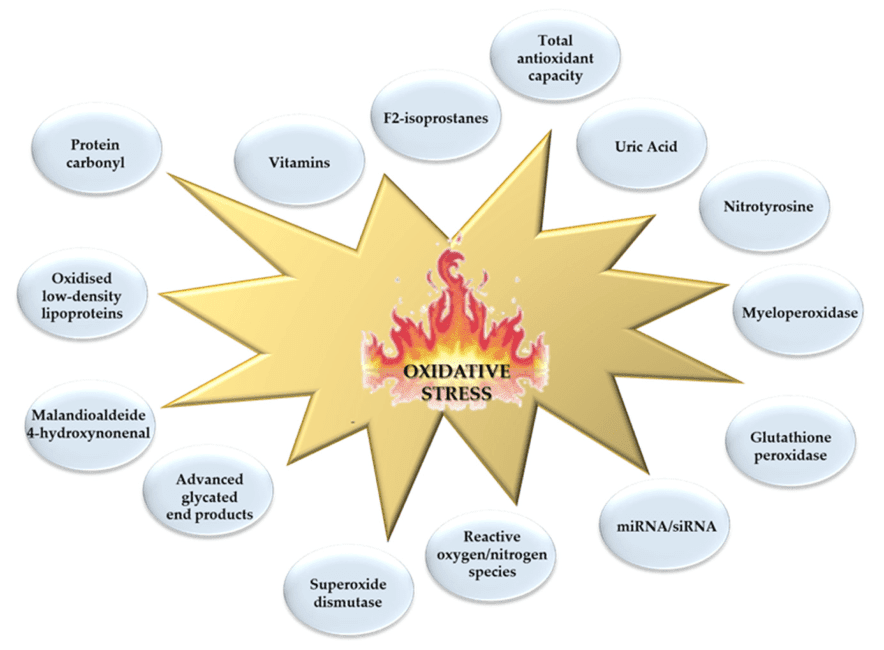
Oxidative Stress
In the world of modern healthcare, understanding the underlying factors that affect our well-being is essential. One such factor is oxidative stress, a complex physiological process that can have a profound impact on our health. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricate mechanisms of oxidative stress, its effects on the body, and how to mitigate its consequences. https://georgetownsuncryo.com/
What is Oxidative Stress?
Oxidative stress is a term that often appears in discussions about health and wellness, but what exactly is it? At its core, oxidative stress is a state in which there is an imbalance between the production of free radicals and the body’s ability to neutralize them. Free radicals are highly reactive molecules that can damage cells, proteins, and DNA. They are produced as natural byproducts of metabolic processes, but their levels can surge due to factors like environmental toxins, poor diet, and stress.
The Role of Free Radicals
Free radicals, specifically reactive oxygen species (ROS), are a natural part of our body’s functioning. They play a crucial role in various physiological processes, such as immune response and cell signaling. However, when their levels become excessive, they can wreak havoc on our health.
- Cellular Damage: One of the primary consequences of high levels of free radicals is cellular damage. These molecules attack cell membranes, proteins, and genetic material, leading to a wide range of health issues.
- Inflammation: Oxidative stress triggers inflammation, a key driver of many chronic diseases. Prolonged inflammation can result in conditions such as arthritis, heart disease, and cancer.
- Aging: Free radicals contribute to the aging process, leading to wrinkles, reduced skin elasticity, and other signs of aging.
- Neurological Disorders: Oxidative stress is also associated with neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
The Body’s Defense Mechanisms
Fortunately, our bodies have evolved to combat oxidative stress through a complex network of antioxidants. Antioxidants are compounds that neutralize free radicals, preventing them from causing harm. Some well-known antioxidants include vitamins C and E, beta-carotene, and enzymes like superoxide dismutase.
- Enzymatic Defense: Enzymes like catalase and glutathione peroxidase work to break down and eliminate harmful free radicals.
- Non-Enzymatic Defense: Non-enzymatic antioxidants, such as vitamins and minerals, play a critical role in quenching free radicals and reducing oxidative stress.
- Dietary Sources: Consuming a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains provides the body with an ample supply of antioxidants. Foods like blueberries, spinach, and nuts are particularly beneficial.
The Consequences of Uncontrolled Oxidative Stress
Oxidative stress isn’t just a theoretical concern; it has real, tangible consequences for our health. Let’s explore some of the conditions and diseases that can result from unchecked oxidative stress.
1. Cardiovascular Disease
Oxidative stress damages blood vessels, promoting the formation of atherosclerotic plaques. This can lead to conditions such as heart disease and stroke.
2. Cancer
Free radicals can alter DNA, increasing the risk of mutations that lead to cancer. Oxidative stress is closely linked to various forms of this disease.
3. Diabetes
Oxidative stress plays a role in insulin resistance and beta-cell dysfunction, contributing to the development of type 2 diabetes.
4. Neurodegenerative Disorders
Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and other neurodegenerative diseases are associated with oxidative stress-induced damage to brain cells.
5. Inflammatory Conditions
Oxidative stress fuels chronic inflammation, a common denominator in conditions like arthritis, asthma, and even allergies.
How to Combat Oxidative Stress
Preventing and mitigating oxidative stress is crucial for maintaining good health. Here are some practical steps you can take to reduce its impact on your body:
1. Balanced Diet
Eating a diet rich in antioxidants can help neutralize free radicals. Consume plenty of fresh fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Berries, leafy greens, and nuts are excellent choices. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
2. Regular Exercise
Exercise stimulates the body’s production of natural antioxidants and enhances overall health. Aim for a mix of cardiovascular and strength-training activities.
3. Stress Management
Chronic stress contributes to oxidative stress. Engage in relaxation techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, and yoga to manage stress effectively.
4. Antioxidant Supplements
In some cases, individuals may benefit from antioxidant supplements, but these should be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
5. Avoid Environmental Toxins
Minimize exposure to environmental toxins, such as pollution and tobacco smoke. These factors can significantly increase oxidative stress.
In Conclusion
Oxidative stress is a complex biological process that can significantly impact our health when left uncontrolled. By understanding its mechanisms and taking proactive steps to mitigate its effects, we can safeguard our well-being and reduce the risk of numerous chronic diseases. https://georgetownsuncryo.com/