Lyme Disease
Lyme disease, often referred to as the “great imitator” due to its ability to mimic the symptoms of various other conditions, is a prevalent and debilitating tick-borne illness. It is essential to gain a comprehensive understanding of this ailment, from diagnosis to treatment, to effectively combat it. In this detailed guide, we will delve into every aspect of Lyme disease, ensuring you’re well-informed about its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and the latest treatment options available. https://georgetownsuncryo.com/
Understanding Lyme Disease
Lyme disease is primarily transmitted through the bite of infected black-legged ticks, commonly known as deer ticks. These tiny arachnids harbor the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi and can transfer it to humans when they attach themselves to the skin. The disease is more common in certain regions, such as the northeastern, north-central, and Pacific coastal areas of the United States.
The Telltale Signs
Recognizing Lyme disease can be challenging as its symptoms can imitate other conditions. Common indications include:
- Bull’s-Eye Rash: One of the most distinct symptoms is a circular rash with a central clearing, resembling a bull’s-eye.
- Flu-Like Symptoms: Early-stage Lyme disease can manifest as fever, chills, fatigue, and body aches, akin to flu symptoms.
- Joint Pain: As the disease progresses, it may lead to joint pain and swelling, particularly in the knees.
- Neurological and Cardiac Issues: In severe cases, Lyme disease can affect the nervous system and heart, leading to complications.
Diagnosing Lyme Disease
Accurate diagnosis of Lyme disease is pivotal to ensuring prompt and effective treatment. Physicians employ a combination of clinical assessment and diagnostic tests.
Clinical Evaluation
A physician will first assess the patient’s medical history and perform a physical examination. This evaluation aids in identifying common symptoms and risk factors associated with Lyme disease.
Diagnostic Tests
Several diagnostic tests can help confirm the presence of Lyme disease:
- ELISA Test: This blood test is the initial step in diagnosing Lyme disease. It detects antibodies against the Borrelia bacterium.
- Western Blot Test: If the ELISA test returns positive or inconclusive, a Western blot test is conducted to confirm the diagnosis.
- PCR Test: Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests are used to detect the genetic material of the Borrelia bacterium. It is particularly useful in the early stages of the disease.
- Cerebrospinal Fluid Analysis: For patients with neurological symptoms, a cerebrospinal fluid analysis may be performed to check for infection in the central nervous system.
Treatment Approaches
Once Lyme disease is diagnosed, the treatment approach may vary depending on the stage and severity of the infection. Here’s an overview of the treatment options:
Antibiotics
The primary treatment for Lyme disease is antibiotics. The choice of antibiotics and duration of treatment depend on the stage of the disease. Commonly prescribed antibiotics include doxycycline, amoxicillin, and cefuroxime.
Prevention
Preventing Lyme disease is paramount, especially if you reside in or frequently visit tick-prone areas. Some preventive measures include:
- Tick Repellents: Use insect repellents containing DEET or permethrin.
- Tick Checks: Regularly inspect your body and clothing for ticks.
- Protective Clothing: Wearing long sleeves and pants, along with tucking pants into socks when venturing into tick-infested areas.
- Tick Removal: Properly removing ticks with fine-tipped tweezers to reduce the risk of infection.
Seeking Professional Guidance
In addition to self-help measures, it’s crucial to consult healthcare professionals for expert advice on tick-borne disease prevention.
Emerging Research and Future Prospects
Medical research is continually evolving, offering new insights into Lyme disease. Recent advancements include improved diagnostic tools, novel treatment options, and ongoing efforts to develop a Lyme disease vaccine. https://www.webmd.com
Final Thoughts
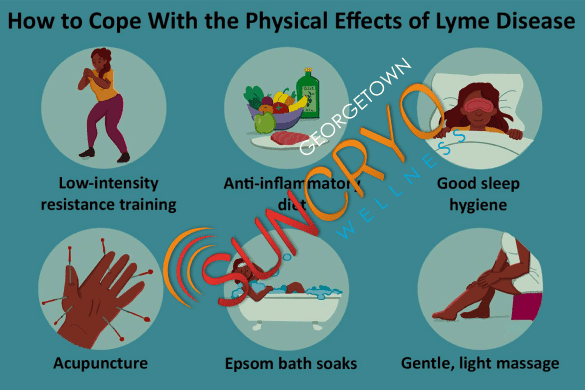
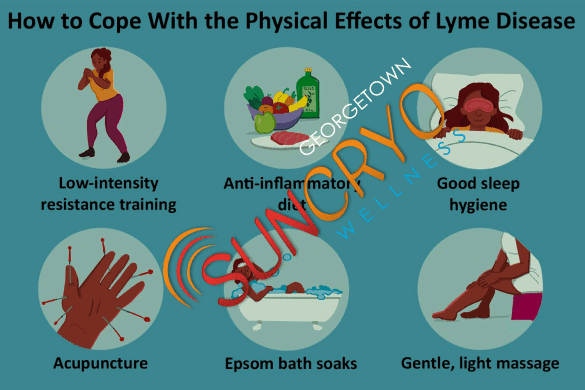
In conclusion, Lyme disease is a complex and often misunderstood illness. To effectively combat it, we must educate ourselves about its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. By staying informed and taking preventive measures, we can reduce the risk of Lyme disease and ensure prompt and effective treatment if needed.
conclusion
the comprehensive exploration of Lyme disease diagnosis and treatment in our ultimate guide has shed light on the complexities of this debilitating illness. We have delved into the intricacies of recognizing the signs and symptoms, the importance of early detection, and the diagnostic tools available. Additionally, we have explored the various treatment options, from antibiotics to alternative therapies, emphasizing the significance of personalized care in managing Lyme disease. https://my.clevelandclinic.org